The manufacturing industry has long been a vital part of the global economy, offering trillions in goods and services to its customers. From cars to phones and everything in between – it’s safe to say that without this sector, we wouldn’t have any of the modern conveniences we enjoy today. But what exactly is manufacturing? What are all the significant parts that make up this complex system?
In this article, we’ll take an in-depth look at the components of modern manufacturing – from raw materials, production processes, and automated machinery to customer orders and beyond. See how everything fits together as we explore what it means for large and small companies when they talk about “manufacturing.”
Table of Contents
Define Manufacturing
Manufacturing is a vital part of our economy; it is taking raw materials and using physical and chemical processes to turn them into products ready for consumers’ use. Manufacturing includes producing anything from automobiles to iPhones, in addition to factory-produced clothing, shoes, electronics, furniture, and even food products.
By utilizing skilled technicians with access to advanced technology, manufacturing ensures fast and efficient production and quality assurance. Not only does this create a variety of excellent products for us to purchase and use every day, but it also provides valuable job opportunities worldwide and helps drive economic growth.
The History Of Manufacturing
Manufacturing has been around since humans first made tools and weapons from stone, wood, and metal. As our technology advanced, manufacturing changed along with it – eventually leading to the development of automated manufacturing processes in the 18th century.
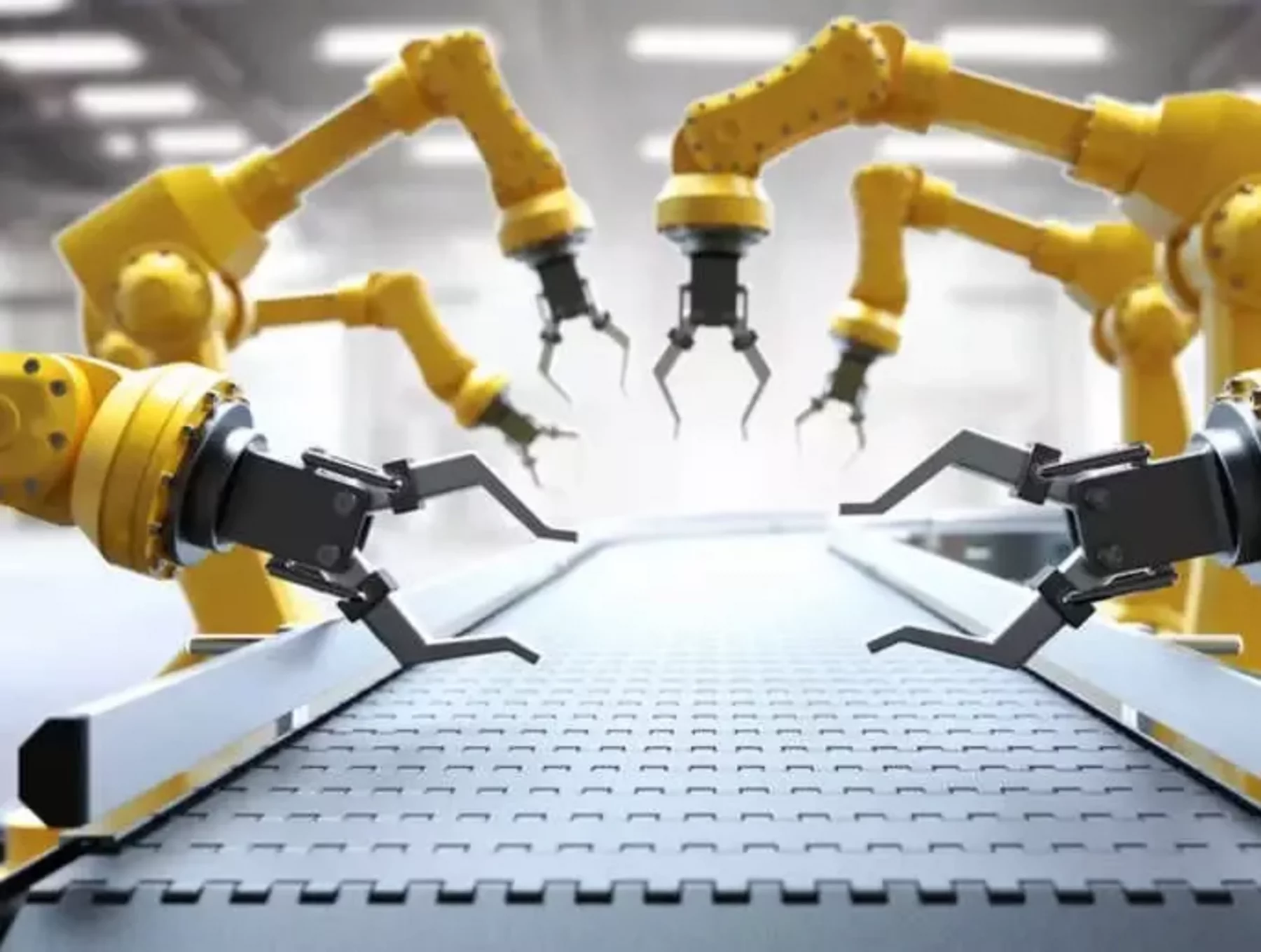
Today’s manufacturing industry is primarily based on automation using robotics and computer-controlled manufacturing systems, which helps increase productivity while maintaining quality control throughout the process. The drive for efficiency has also led to a focus on making products faster than ever before, which provides companies with an edge over their competitors.
The Different Types Of Manufacturing
Manufacturing falls into two categories: discrete manufacturing and process manufacturing. Discrete manufacturing produces items such as cars, phones, or other products with a specific end goal. Production processes are typically well-defined and use specialized machinery to assemble parts faster and more accurately than manual labor.
On the other hand, process manufacturing involves producing goods through multiple steps with an ongoing input of materials. This type of manufacturing can involve anything from foodstuffs to chemicals, paints, and more. In contrast to discrete manufacturing, process manufacturing often has less control over final product specifications due to its focus on continuous inputs, which may vary depending on various factors, including raw material quality and environmental conditions.
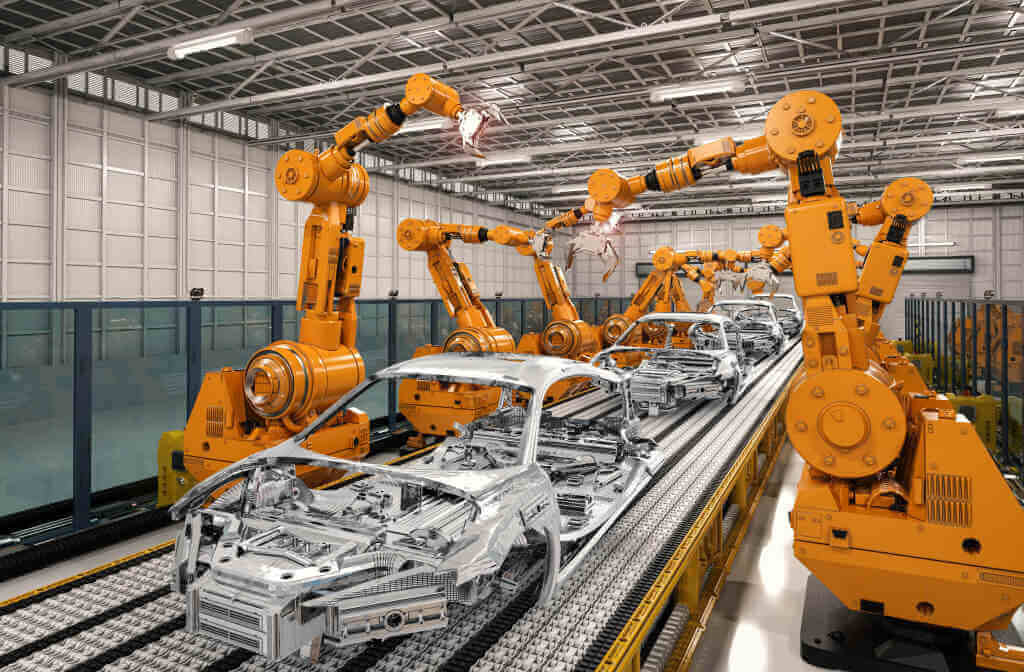

The Benefits Of Manufacturing
Manufacturing is crucial to the world’s economy, providing jobs and driving growth. By turning raw materials into valuable products, manufacturing helps keep prices down while ensuring quality control. Additionally, manufacturing can contribute to increased sustainability; by producing items locally, companies can reduce their environmental impact while still satisfying customer demand.
Modern manufacturing also brings new opportunities for businesses to increase efficiency with automation. Automated manufacturing robots can be used across industries to quickly and accurately assemble components without needing constant supervision – resulting in faster production cycles and more excellent reliability.
Manufacturing robots are becoming more efficient and reliable each year, allowing businesses to produce quality goods on a large scale. By harnessing this technology, manufacturing companies can ensure their products are of the highest quality while remaining competitive in an ever-changing global market.
The Challenges Of Manufacturing
Despite its many benefits, manufacturing has its challenges. One of the most significant issues facing manufacturers today is the ever-increasing cost of raw materials and labor. It can make it difficult for companies to remain competitive in the global marketplace while maintaining their quality standards.
In addition, some countries have stricter regulations regarding environmental impact than others. Companies must be aware of these regulations when manufacturing in different countries to avoid costly fines or delays in production. It can be especially difficult for companies that outsource manufacturing to different parts of the world, as they may be unaware of specific regulations once it is too late.
Finally, there are also challenges associated with automated manufacturing robots. As technology advances, robots become increasingly expensive to purchase and maintain, and companies must weigh the costs of automation against the potential benefits before investing in robotics. Additionally, robots require maintenance and programming; if something goes wrong with a robot, it can cause costly production delays or even lead to product defects.
The Future Of Manufacturing
As the cost of raw materials and labor continues to rise, manufacturers must look for alternative ways to reduce costs while maintaining quality standards. Automation will continue to play a significant role in manufacturing as robots become increasingly efficient and reliable. Companies that remain up to date with the latest technology can gain an edge over their competition by producing goods more quickly and accurately than ever before.
In addition, companies may also benefit from using sustainable materials such as recycled plastics or bioplastics in their production processes. By replacing traditional materials with more eco-friendly alternatives, manufacturers can help protect the environment and reduce their costs while still producing high-quality products.