Table of Contents
What are Lab-Grown Diamonds?
The Science Behind Lab-Grown Diamonds
Lab-grown diamonds, also known as synthetic or cultured diamonds, are diamonds that are produced in controlled laboratory environments using advanced technological processes that mimic the natural conditions under which diamonds form in the Earth. These processes replicate the high pressure and high temperature conditions that occur in the Earth’s mantle, creating diamonds that are chemically, physically, and optically identical to natural diamonds.
Difference Between Natural and Lab-Grown Diamonds
While natural diamonds take millions of years to form, lab-grown diamonds can be created in just a few weeks. Both types of diamonds are made of carbon atoms arranged in a crystal structure, but the key difference lies in their origin. Natural diamonds are mined from the Earth, while lab-grown diamonds are created in laboratories.
Despite the differences in their formation, lab-grown diamonds have the same chemical composition, hardness (10 on the Mohs scale), and brilliance as mined diamonds. This makes them nearly indistinguishable to the naked eye.
Why Lab-Grown Diamonds Are Gaining Popularity
Ethical Sourcing and Sustainability
One of the driving forces behind the rise of lab-grown diamonds is the growing consumer demand for ethical sourcing. Many traditional diamond mines have been associated with human rights violations, child labor, and environmental degradation. The Kimberley Process aimed to curb the trade of conflict diamonds, but issues remain.
Lab-grown diamonds, on the other hand, are created in controlled environments, which means they don’t involve the ethical concerns tied to diamond mining. With a growing emphasis on sustainability and ethical consumerism, lab-grown diamonds are viewed as a more responsible choice for consumers who want a beautiful, conflict-free stone.
Cost-Effectiveness
Another reason for the increasing popularity of lab-grown diamonds is their cost-effectiveness. Lab-grown diamonds typically cost between 20% to 40% less than their natural counterparts. This price difference is due to the fact that lab-grown diamonds are produced in a more controlled environment and don’t require expensive mining operations, which significantly reduces their production costs.
For buyers who want the look and feel of a diamond without the high price tag, lab-grown diamonds offer an affordable alternative.
Changing Consumer Preferences
Consumers today are increasingly prioritizing sustainability, transparency, and ethical production in their purchasing decisions. Millennials and Gen Z, in particular, are driving the demand for lab-grown diamonds. They are not only more environmentally conscious but also more willing to consider new technologies and alternatives to traditional products.
As a result, lab-grown diamonds are becoming a popular choice for engagement rings, wedding bands, and other fine jewelry, as they offer a blend of luxury and social responsibility.
The Process of Creating Lab-Grown Diamonds
High Pressure High Temperature (HPHT) Method
The HPHT method is one of the most common techniques used to create lab diamonds are the future. It mimics the natural process that occurs deep within the Earth’s mantle, where carbon atoms are subjected to intense pressure and temperature. In this method, a small diamond seed is placed in a chamber, and carbon is added. The pressure and temperature are then increased to the point where the carbon crystallizes around the seed, forming a diamond.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) Method
The CVD method is another popular technique used to grow diamonds in a lab. Unlike HPHT, CVD involves using a gas mixture (usually methane) in a vacuum chamber, where it is ionized into plasma. This plasma breaks the methane into carbon atoms, which then deposit onto a diamond seed and crystallize to form a diamond.
How CVD Works in Diamond Creation
CVD diamonds are created layer by layer, with the carbon atoms bonding to the seed to form a diamond structure. This process allows for more precision and control, resulting in diamonds with fewer inclusions and greater clarity. The CVD method also allows for the creation of larger diamonds, making it a popular choice for jewelry manufacturers.
Benefits of Lab-Grown Diamonds
Environmental Impact: Lower Carbon Footprint
Lab-grown diamonds are environmentally friendly compared to traditional diamond mining. Mining for natural diamonds can cause significant environmental damage, including habitat destruction, water pollution, and carbon emissions. In contrast, lab-grown diamonds typically have a much lower carbon footprint because they don’t require large-scale mining operations.
The CVD and HPHT methods used to create lab-grown diamonds require far less energy and are more sustainable. For eco-conscious consumers, lab-grown diamonds offer a beautiful way to enjoy luxury without harming the planet.
Traceability and Transparency in the Supply Chain
Another significant advantage of lab-grown diamonds is the traceability of their origin. Unlike natural diamonds, whose supply chains can sometimes be opaque, lab-grown diamonds come with a clear history, as they are created in a controlled environment. This level of transparency provides consumers with peace of mind, knowing exactly where their diamonds come from and how they were made.
Identical to Natural Diamonds: Quality and Durability
Lab-grown diamonds are made from the same material as natural diamonds, meaning they have the same hardness, brilliance, and clarity. In fact, some lab-grown diamonds even have fewer inclusions and imperfections compared to natural diamonds, making them a high-quality choice for those who want a flawless stone.
Challenges and Misconceptions About Lab-Grown Diamonds
The Perception of Value and Rarity
One of the biggest challenges lab-grown diamonds face is the perception of value. Natural diamonds have long been associated with rarity and luxury, and many consumers believe that lab-grown diamonds, being man-made, are less valuable. However, as consumer awareness grows, more people are recognizing that lab-grown diamonds are just as valuable in terms of quality, and they are increasingly seen as a better alternative.
The Issue of Certification and Disclosure
While lab-grown diamonds are ethically sourced, there has been some confusion over certification and disclosure. Some jewelers may not disclose whether a diamond is natural or lab-grown, leading to potential consumer confusion. Fortunately, there are certification bodies like the Gemological Institute of America (GIA) and International Gemological Institute (IGI) that certify both natural and lab-grown diamonds to ensure transparency in the industry.
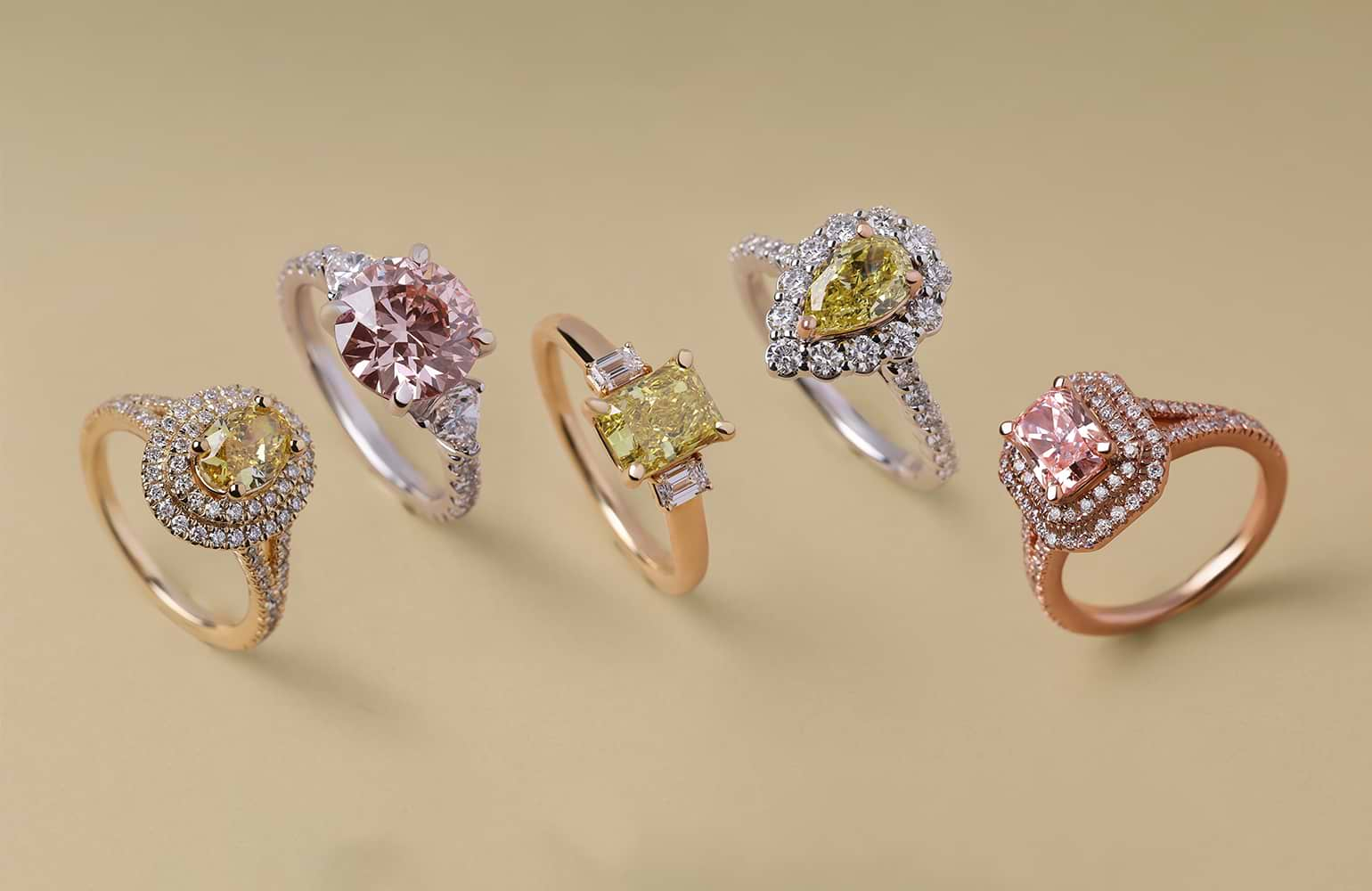
Lab-Grown Diamonds vs. Natural Diamonds: A Comparison
Price Comparison: Lab-Grown vs. Mined Diamonds
Lab-grown diamonds are significantly more affordable than natural diamonds. For the same size and quality, a lab-grown diamond can cost anywhere from 20% to 40% less than a natural diamond. This price difference makes lab-grown diamonds an attractive option for consumers looking to get more value for their money.
Durability and Hardness: Are Lab-Grown Diamonds Less Strong?
Lab-grown diamonds are just as durable and strong as natural diamonds. Both types of diamonds rank a perfect 10 on the Mohs hardness scale, meaning they are virtually scratch-resistant and ideal for everyday wear. Lab-grown diamonds are no less durable than natural lab grown diamonds; they’re just created in a different way.
Resale Value: Will Lab-Grown Diamonds Hold Their Worth?
The resale value of lab-grown diamonds is currently lower than that of natural diamonds. While lab-grown diamonds offer great value for money upfront, the market for resale is still evolving. However, as lab-grown diamonds become more mainstream, their resale value may improve over time.
The Future of Lab-Grown Diamonds in the Jewelry Market
The Rise of Lab-Grown Diamonds in Engagement Rings
Lab-grown diamonds are quickly gaining popularity in the engagement ring market, as couples look for alternatives to traditional diamonds. With the rising demand for ethical, sustainable products, lab-grown diamonds are becoming a popular choice for those who want a beautiful ring without the ethical concerns.
Lab-Grown Diamonds and Sustainability Trends in Fashion
Fashion jewelry is also embracing lab-grown diamonds, with designers incorporating them into rings, necklaces, earrings, and bracelets. As sustainability becomes a more significant factor in fashion, lab-grown diamonds are expected to play an even more prominent role in the jewelry market.
Lab-Grown Diamonds in Fashion Jewelry
From luxury designers to affordable fashion brands, lab-grown diamonds are making their way into the mainstream. As consumer demand for sustainable products continues to rise, we can expect lab-grown diamonds to be a staple in both fine and fashion jewelry.
Lab-Grown Diamonds in Other Industries
Lab-Grown Diamonds in Technology and Electronics
Beyond jewelry, lab-grown diamonds are finding uses in technology and electronics. Their unique properties, such as high thermal conductivity and electrical insulation, make them ideal for applications in semiconductors, high-performance electronics, and even quantum computing.
Medical Uses of Lab-Grown Diamonds
Lab-grown diamonds are also being explored for use in medical applications, such as in the creation of ultra-durable tools for surgeries or in advanced imaging technologies. Their hardness and biocompatibility make them an appealing option for the medical field.
Conclusion: Why Lab-Grown Diamonds Are the Future
Lab-grown diamonds are undeniably the future of the diamond industry. With their ethical sourcing, environmental benefits, affordability, and identical quality to natural diamonds, they offer a compelling alternative to traditional diamonds. As technology continues to improve and consumer demand grows, lab-grown diamonds will likely become even more prevalent, reshaping the way we think about diamonds in the years to come. Whether you’re purchasing a diamond engagement ring, a piece of fashion jewelry, or investing in technological advancements, lab-grown diamonds are here to stay.